Black Market Bazaar: The Ascent and Decline of Underground Web Commerce
Recently, the dark web has appeared as a shadowy side of the online world, a space where secrecy is paramount and illegal commerce flourishes. Dark web markets, often called as darknet marketplaces, have enthralled both users and authorities alike with their covert goods, ranging from illegal drugs and stolen data to individualized services and arms. The attraction of these markets lies not only in their products but also in the lack of central authority of transactions, allowing users to trade without standard regulation.
Nevertheless, the rise of these secretive platforms has been met with heightened oversight and enforcement actions from law enforcement agencies worldwide. As authorities become more adept at penetrating and dismantling these operations, the ecosystem of dark web trade is in a state of change. This dance between new ideas and control defines the course of the underworld bazaar, where fresh marketplaces rise from the remnants of past marketplaces, and the patterns of hidden transactions and exposure continues to shape the dark web.
Origins of the Deep Web
The genesis of the dark web can be followed back to the beginnings of the internet when confidentiality and anonymity were essential issues for developers and internet participants alike. In the mid-1990s, the American Naval Research Laboratory created the Tor project to facilitate protected interactions for government entities. Tor, which stands for The Onion Router, was developed to safeguard the persons and locations of its users by sending internet traffic through numerous servers and encrypting data at each step.
As the tech matured, the possibilities for the deep web expanded. By the 2000s, individuals began to leverage Tor for other safe communication. It became a refuge for those wishing to talk about sensitive topics without worry of monitoring and restrictive oversight. This led to the emergence of various platforms and forums where users could engage in secrecy. The allure of confidentiality drew a varied crowd, from activists and reporters to individuals seeking a way to participate in illicit activities.
By the late 2000s, deep web markets began to prosper. These online bazaars offered a range of items and services, from illegal narcotics to cybersecurity tools. The use of digital currencies for exchanges further facilitated this hidden commerce, as it allowed for additional levels of disguise. As dark web markets gained popularity, they became a key focus for law enforcement agencies, igniting a endless chase that persists to this day.
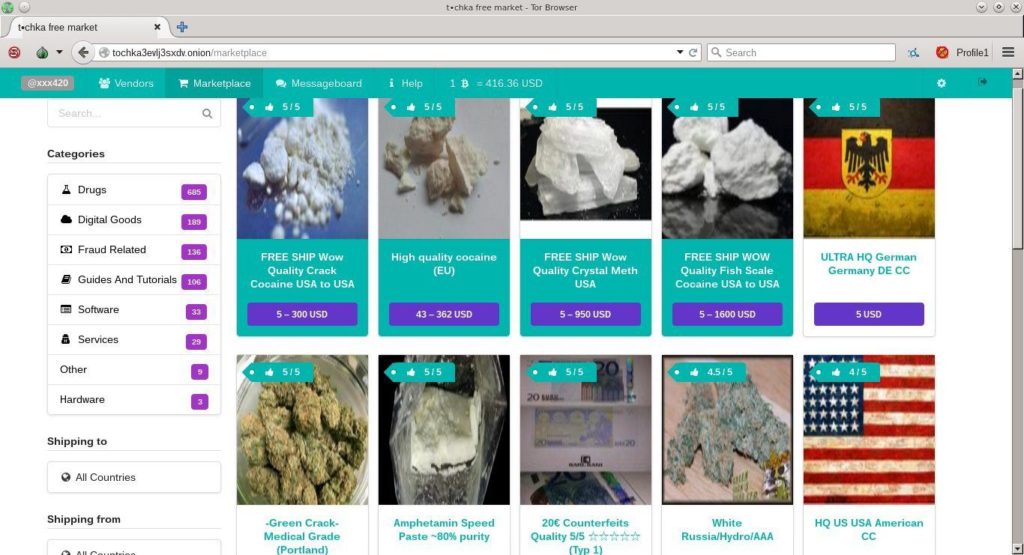
Key Players in Darknet Marketplaces
The scene of darknet marketplaces is shaped by various important participants who play a role its distinct ecosystem. Vendors are often seasoned dealers who concentrate in particular products, ranging from illegal narcotics to forged goods. They utilize encryption and secrecy to protect their identities while navigating the challenges of transactions on the dark web. Some sellers establish a name through buyer feedback, which can greatly impact their ability to attract buyers and keep a lucrative operation.
Consumers in darknet markets are similarly motivated by varied reasons, including the availability of products that may be illegal or challenging to acquire in traditional marketplaces. These individuals are generally tech-savvy and recognize the importance of maintaining secrecy, often using crypto assets to carry out transactions. Some buyers are risk-taking shoppers seeking unique finds, while others are more serious, drawn to the temptation of acquiring illicit drugs or other forbidden goods without the risk of detection in the offline space.

Market administrators and overseers play a crucial role in maintaining the functionality of these platforms. They supervise operations, impose rules, and make certain that transactions advance efficiently. Many sites also provide support services, such as issue resolution and third-party payment services, designed to safeguard both buyers and vendors. This threefold of players creates a dynamic environment where trust and security are paramount, despite the inherent risks involved in the clandestine exchange.
The Decrease of Dark Web Trade
The diminishing of trade on the dark web can be ascribed to growing law enforcement initiatives focused on illegal activities. Governments around the globe have become more skilled at tracking and charging individuals involved in dark web transactions. Crackdowns like Silk Road and AlphaBay marketplace led to significant arrests, which created a chilling effect on both sellers and customers. As the risks of engaging in dark web markets increased, many users began reevaluate their participation in these illicit platforms.
Another factor contributing to the diminishing is the emergence of alternative solutions for accessing illegal goods and services. darkmarket was once viewed as the chief avenue for such deals, but developments in tech have led to the rise of readily available black markets on the clearnet. This shift has pulled many users away from the anonymity and risks associated with dark web markets, opting for safer and more accessible and perceived safer options.
Finally, the general market saturation has played a role in the diminishing of dark web trade. As many emerging platforms emerged, competition increased among vendors, often leading to a diminution in product quality and trustworthiness. Consumers began to lose confidence in the distributed market, understanding that the promised anonymity did not necessarily guarantee security or high quality. Combined with the tightening of law enforcement and the arrival of new approaches, the dark web trade has experienced a marked decline in user engagement and transaction volume.